Institute of Software Technology and Interactive Systems
Information & Software Engineering Group
Music Information Retrieval

Our team has a strong background in Information Retrieval in general, but particularly also in Music Information Retrieval, since 1999.
Facing larger and larger collections of audio, both in private and professional domains, we are researching for ways to make these massive volumes of content accessible to the users. Currently, the search in music repositories is mostly limited to textual queries on meta-data fields, which moreover require manual annotation effort beforehand.

Our research focuses on various methods of indexing and structuring audio collections, as well as providing intuitive user interfaces to facilitate exploration of musical libraries. Machine learning techniques are used to e xtract semantic information, group audio by similarity, or classify it into various categories. We developed advanced visualization techniques to provide intuitive interfaces to audio collections on standard PC as well as mobile devices. Our solutions automatically organize music according to its sound characteristics such that we find similar pieces of music grouped together, enabling direct access to and intuitive instant playback according to one's current mood.
Have a look at our leaflet/brochure (PDF) for a brief overview of our topics.
The following page gives a comprehensive overview of our research topics. Click on each topic to find out more details about the different approaches. For further inquiries, please contact Prof. Andreas Rauber.
NEWS: We organized the 2nd Waves Vienna Music Hackday on 30 Sep + 1 Oct 2016.
Audio Feature Analysis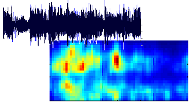
We are researching advanced methods for extracting semantic information from music, such as rhythm, presence of voice, timbre, etc, using digital signal processing and psycho-acoustics. These feature extraction algorithms are the basis to many subsequent tasks, like automatic music categorization and organization. [more...] |
Music Classification
Applying machine learning methods and employing the features calculated from audio signal analysis we built a system performing categorization of music pieces into a pre-defined taxonomy, corresponding to the user's likes. The system has to be trained with a number of examples and is then able to categorize music into different classes, e.g. music genres (classical, jazz, hip hop, electronic, ...) or also identify artists. We also investigate combination of textual with audio information for music classification, and the recognition of moods and emotions in music. [more...] |
Benchmarking
The Million Song Dataset (MSD) enables testing Music Information Retrieval methods on a large-scale
dataset. The MSD comes as a collection of meta-data such as the song names, artists and albums, together with a set of
features extracted with the The Echo Nest services. |
PlaySOM - Organisation of Music Archives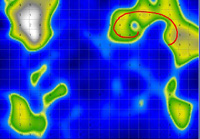
The PlaySOM project is about unsupervised organisation of whole music archives, which means that no training of the system is necessary. We apply the Self-Organizing Map (SOM) algorithm on audio features and are thus able to organize a music archive on an intuitive map, grouping audio tracks by their perceived acoustic similarity. Music with a similar style is located close to each other, building clusters (or islands), while music with different style is located farther away. As the name says, the system is compeletely self-organizing, and thus overcomes traditional genre boundaries and adapts individually depending on the music archive used. [more...] |
PocketSOMPlayer - Browsing Music on Mobile Devices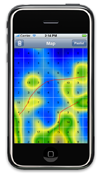
Large music collections are becoming more and more important also for the mobile user. People are able to carry their complete audio collection with them on portable devices. Especially these small mobile devices are in a need of intuitive and intelligent access to music collctions. Manually searching through directory structures and sorting music into playlists is no way to enjoy music, especially when one wants to listen to music of a particular mood. We are bringing the PlaySOM concept also to state-of-the-art mobile devices, enabling a range of new scenarios. [more...] |
Map of Mozart
We extracted acoustic features from the complete works of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and created an interactive Map of Mozart. The map provides an immediate overview of all works by Mozart. The shape of the map was chosen to resemble Mozart's silhouette by using the MnemonicSOM algorithm. A semi-transparent layer enables the visualization of both Mozart's head and the Islands of Music metaphor for intuitive browsing and selection of the music. Using the PlaySOM application, all pieces of music ever composed by Mozart can thus be retrieved, and the web demo shows the concept on a number of freely available recordings. [more...] |
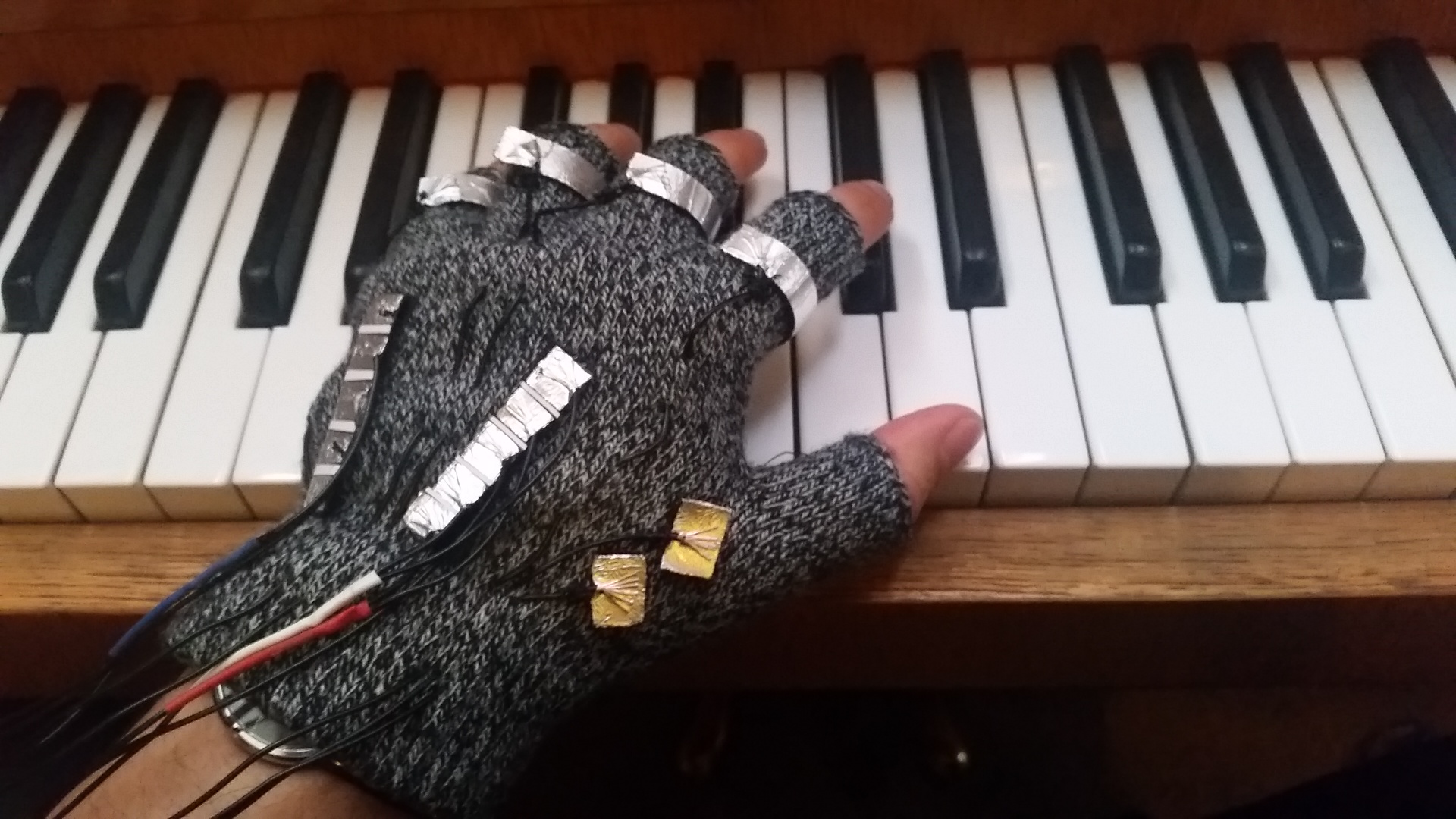
GloveFX |
Beat Circles
Beat Circles represents music graphically in real-time in a aesthetically pleasing and informative way. It allows users that are not proficient with music to better understand and interact with the piece using intuitive creative thought. [more...] |
The MediaSquare - 3D Multimedia Environment
We developed a 3D Multimedia environment where users are impersonated as avatars enabling them to browse and experience multimedia content by literally walking through it. Users may engage in conversations with other members of the community, exchange experiences or simply enjoy the featured content. [more...] |
Query by Example for MIDI files |
Audio Chord Detection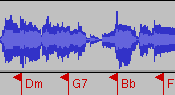
We developed a chord detection algorithm incorporating music theoretical knowledge in the form of key detection, beat tracking and chord-change frequencies improving the detection of chords in audio without restricting it to a narrow range of applicable music styles. [more...] |
Audio Source Separation
The goal of (blind) audio source separation is to separate audio tracks into their sources, i.e. sounds or tones from
instruments. |
Acoustic Evaluation of Music Similarity
The evaluation of "similarity" between pieces of music is a non-trivial task because human cognition of music and perception of similarity is biased by subjective interpretation and reasoning based on knowledge and conventions of the real world. We developed a tool enabling efficient acoustic evaluation of music similarity, making use of dynamic sequential and parallel playback, also allowing to explore and analyze structured audio repositories much faster and more efficiently. [more...] |
Automatic Audio SegmentationAutomatic audio segmentation aims at extracting information on a songs structure, i.e. segment boundaries and recurrent structures (i.e. verse, chorus, bridge etc.). This information can be used to create representative song excerpts, to facilitate browsing in large music collections or to improve other applications such as music categorization. [more...] |
SOM Racer - interactive music explorer
SOMRacer combines the functionality of the PlaySOM and PocketSOMPlayer applications with the look-and-feel of the classic open-source game TUX Racer. Self Organizing Maps serve as three-dimensional music landscapes, which can be explored by the player. The collected music tracks are exported as playlist. [more...] |
Visualization Enhancements
PlaySOM provides a number of intuitive visualization methods making browsing through music a pleasure. We implemented the U-Matrix, showing distances between neighbouring clusters, Smoothed Data Histograms, showing a methaphor of Islands of Music, as well as Weather Charts, and more. Research on visualization methods is continuing to provide the most enjoyable means of access to the wealth of music possible. [more...] |
SOMeJB - The SOM-enhanced JukeBox
SOMeJB, the SOM-enhanced JukeBox, commenced in 1999, established the basis for our browsing interfaces to music archives. The SOMeJB Music Digital Library Project aims at creating a browsable music archive by combining a variety of technologies from the fields of audio processing, neural networks, and information visualization, to create maps of music archives. It is based on the self-organizing map (SOM), a popular unsupervised neural network and its extension GHSOM. [more...] |
| top |
last edited 27.07.2015 by Thomas Lidy
|



