Information Management and Preservation
Information and Software Engineering Group (IFS)Institute of Information Systems Engineering (ISE)
Vienna University of Technology
ROMOR
(2016-2019) ROMOR aims over the course of three years to build capacity on research output management in four leading PS HEIs by establishing Open Access Institutional Repositories (OAIR). The training which is required to establish these repositories, and then their implementation, population and management will be the core of the project. Learning outcomes from these activities will also be shared and disseminated in a variety of ways, including the establishment of mechanisms to assist proactively other institutions in setting up and managing repositories. This Project aims to improve not only the visibility and the management of scientific research, but also to support the advocacy in support of open access to research outputs and to foster scholarly communication and coordination between PS HEIs.
MusicBricks
(2015-2016) Immersive and engaging participatory and collaborative modes of production are characteristic of the emerging creative economies of music media and require novel ICT solutions. The most innovative ICT solutions in this sector come from the top EU research centres. The MusicBricks project exploits the creative and commercial possibilities of music technologies by piloting innovative musical tools with the new generation of SME digital makers and content creators, and leverages the state-of-the-art European research, by providing a compendium of physical, virtual and programming interfaces, thus allowing creative developers easy access to the core building blocks of music.
MusicBricks thus provides a pathway for research to reach a wider community of Creative SME innovators, thereby contributing to cultural and economic output right across the creative sector. Our aim is to transfer state-of-the-art ICT to Creative SMEs in order to develop novel business models.
ADmIRE

(2014-2017) Information Retrieval on the World Wide Web functions very effectively and efficiently. These search tools are specifically designed as multi-purpose tools, applicable in as wide an array of situations as possible. Nevertheless, all information is not equal. There are areas for which these tools are conceived too broadly to be useful:
- health or biomedical information
- intellectual property information
- social science publications
- blogs
- press photographs
- ...
A search in one of these domains is called a domain-specific search. Such a search is specific in terms of the collection of documents indexed, search refinements arising from the domain characteristics, domain coverage specificity, types of multimodal data (e.g. images, chemical formulae) present in the documents, and the end users and their tasks.
BENCHMARK DP
(2012-2015) Benchmark DP is developing the first coherent, systematic approach to assess and compare digital preservation processes, systems, and organizational capabilities.
Current theoretical frameworks, engineering approaches and technologies in ICT are not sufficiently capable of efficiently and effectively sustaining the authenticity, understandability and usability of digitally encoded information over time. From its origin in cultural heritage and eScience, digital preservation (DP) has emerged as a key challenge for information systems (IS). Yet, there is a profound lack of theoretically sound and verifiable frameworks to address digital longevity. Currently, numerous strands of applied DP research are hitting a glass ceiling.
Benchmark DP will advance the fundamental understanding of and capacity for digital longevity in ICT by creating theoretical frameworks and quantitative benchmarks. By providing the first systematic, quantified approach to measuring, controlling and improving DP processes and organisational capabilities, Benchmark DP will enhance the ability of organisations to control and improve processes for information management and IS design to achieve desired levels of longevity.
ELIAS
(2011-2016) Although the speed of computers and volume of information has grown exponentially since the first search engines were created in the 1950s, the methods used to test state of the art information access systems have changed little. However, there is growing scientific evidence of a need for a complete testing overhaul: producing novel evaluation methods that take a user-oriented perspective on assessing the effectiveness of information access systems. The proposed network will establish a research and training programme for the evaluation of information access systems which will define a new measurement paradigm based on so-called living laboratories.
KHRESMOI
(2011-2014) Khresmoi aims to develop a multi-lingual multi-modal search and access system for biomedical information and documents. This will be achieved by (1) Effective automated information extraction from biomedical documents, including improvements using crowd sourcing and active learning, and automated estimation of the level of trust and target user expertise; (2) Automated analysis and indexing for medical images in 2D (X-Rays), 3D (MRI, CT), and 4D (MRI with a time component); (3) Linking information extracted from unstructured or semi-structured biomedical texts and images to structured information in knowledge bases; (4) Support of cross-language search, including multi-lingual queries, and returning machine-translated pertinent excerpts, and (5) Adaptive user interfaces to assist in formulating queries and display search results via ergonomic and interactive visualizations. The research will flow into several open source components, which will be integrated into an innovative open architecture for robust and scalable biomedical information search.
SCAPE
(2011-2014) The SCAPE project will enhance the state of the art of digital preservation in three ways: by developing infrastructure and tools for scalable preservation actions; by providing a framework for automated, quality-assured preservation workflows and by integrating these components with a policy-based preservation planning and watch system. These concrete project results will be validated within three large-scale Testbeds from diverse application areas: Digital Repositories from the library community, Web Content from the web archiving community, and Research Data Sets from the scientific community. Each Testbed has been selected because it highlights unique challenges. SCAPE will develop scalable services for planning and execution of institutional preservation strategies on an open source platform that orchestrates semi-automated workflows for large-scale, heterogeneous collections of complex digital objects.
TIMBUS
(2011-2014) The digital preservation problem is well-understood for query-centric information scenarios but has been less explored for scenarios where the important digital information to be preserved is the execution context within which data is processed, analysed, transformed and rendered. Furthermore, preservation is often considered as a set of activities carried out in the isolation of a single domain, without considering the dependencies on third-party services, information and capabilities that will be necessary to validate digital information in a future usage context. TIMBUS will endeavour to enlarge the understanding of DP to include the set of activities, processes and tools that ensure continued access to services and software necessary to produce the context within which information can be accessed, properly rendered, validated and transformed into knowledge. One of the fundamental requirements is to preserve the functional and non-functional specifications of services and software, along with their dependencies. ß
APARSEN
(2011-2014) Digital preservation offers the economic and social benefits associated with the long-term preservation of information, knowledge and know-how for re-use by later generations. However, digital preservation has a great problem, namely that preservation support structures are built on projects which are short lived and is fragmented. The unique feature of APARSEN is that it is building on the already established Alliance for Permanent Access (APA). APARSEN will bring together a wide range of experts in digital preservation including academic and commercial researchers. APARSEN will help to combine and integrate these programmes into a shared programme of work, thereby creating the pre-eminent virtual research centre in digital preservation. It provides a natural basis for a longer term consolidation of digital preservation research and expertise.
MUMIA
(2010-2014) The tremendous power and speed of current search engines to respond, almost instantaneously to millions of user queries on a daily basis is one of the greatest successes of the past decade. While this technology empowers users need to extract relevant information from the hundreds of thousands of terabytes of existing data available on the web, the next decade presents many new grand challenges. This next wave of search technology is faced with even greater demands, not only in terms of volume of requests, but also in terms of the changes to the content available, and the dynamics of Web 2.0+ data being produced. These increased and new demands mean that search technology must be able to search, filter, extract, combine, integrate, and process multiple and distributed sources of multilingual content, delivered to an even wider global audience and variety of population. Inevitably, Multilingual and Multifaceted Interactive Information Access (MUMIA) research and development will be a key part of the next generation of search technology. Machine Translation (MT), Information Retrieval (IR) and Multifaceted Interactive Information Access (MIIA) are three disciplines which address the main components of MUMIA.
PROMISE
(2010-2013) PROMISE will provide a virtual laboratory for conducting participative research and experimentation to carry out, advance and bring automation into the evaluation and benchmarking of such complex information systems, by facilitating management and offering access, curation, preservation, re-use, analysis, visualization, and mining of the collected experimental data. PROMISE will:
- foster the adoption of regular experimental evaluation activities;
- bring automation into the experimental evaluation process;
- promotecollaboration and re-use over the acquired knowledge-base;
- stimulate knowledge transfer and uptake.
IMPEX
(2010-2013) The constantly increasing number of yearly patent applications leads to an increased workload at the patent offices, raising the need for applications and systems that help the patent expert to faster evaluate an application. Up to now, all the software solutions for mining of patents use textual cues only. Hence, important information contained in patent drawings is inaccessible to automated analysis and retrieval. As a result drawings are sometimes misused to "hide" information and to trick full text search systems. Thus the complex task of manually analysing and comparing drawings is left to the expert, which in turn leads to high financial costs. This situation demands the development of innovative algorithms for the mining of patent images (e.g. information extraction, linking and image based search). This will help patent offices to cope with the ever increasing number of filings.
CHORUS+
(2010-2012) CHORUS+ aims to create the conditions of mutual information exchange and cross fertilisation between the FP7 projects in the search-engines domain and the recently launched national and international initiatives in this area. A particular emphasis on setting concrete R&D and industrial objectives for multimedia search in Europe is planed through the implementation of discussion groups limited to selected representatives (industry, academia) and the organisation and on open participation at workshops, conferences and summer schools.
The Essence of Patent Retrieval
(2009-2012) In this project, an alternative way to capture the concept of a patent will be explored. This will investigate logic or semi logical features of expression in patent text. There are some grammar models that try to capture the semantics of a sentence i.e. leaving the surface base of a sentence, which is represented by the sentence words, and transforming sentence into a semantic representation format. Examples of grammar models that with different methods transform surface base to semantic representation are: Head-driven Phrase Structure Grammar, Construction Grammar, and Frame semantics.
(2009-2011) DME is a research studio as part of the Research Studios Austria programme of the Austrian Research Promotion Agency (Österreichische Forschungsförderungsgesellschaft, FFG). It conducts industry-oriented research and development in the field of digital preservation. The aim of the DME is the development of preservation solutions for the industry with a special focus on SMEs. The core research aspects of the research studio are:
- Workflow based support for business archiving solution: Compliances with international standards and best practice models, integration into existing document management systems
- Long term preservation of multimedia content: Research on preservation strategies for multimedia content and systems for archiving embedded multimedia content (wikis, online archives, etc.)
- Archiving solutions for small institutions and SOHOs (Small offices and home offices): Research on a fully-automated archiving systems for users with limited know-how and awareness of digital preservation, development of a prototype archiving system
IMPACT
Austrian Academic Exchange Service Project on Improving Music genre classification Performance by a novel Approach of Combining audio and symbolic music descriptors. (2007-2009)
PLANETS
Digital media have become the dominant way that we create, shape, and exchange information. Unlike paper, however, we have very limited abilities to ensure that today's digital information will be accessible in 10, 50, or 100 years. Unless we act now, we will lose access to the first decades of the digital era, and future generations will see a gaping hole in their cultural and scientific record. The Planets project brings together European National Libraries and Archives, leading research institutions, and technology companies to address the challenge of preserving access to digital cultural and scientific knowledge. The four year project is funded by the European Commission Information Science and Technologies Framework Programe 6 Call 5 (FP6 Call 5).
DPE
Electronic resources are a central part of our cultural and intellectual heritage; but this material is at risk. Digital memory needs constant management, using new techniques and processes, to contain such risks as technological obsolescence. Risk begins before the digital record is created and continues for as long as the digital object needs to be retained. Digital preservation is too big an issue for individual institutions or even sectors to address independently. Concerted action at both national and international level is required. DigitalPreservationEurope facilitates pooling of the complementary expertise that exists across the academic research, cultural, public administration, and industry sectors in Europe.
DELOS
The DELOS network, started in January 2004, intends to conduct a joint program of activities aimed at integrating and coordinating the ongoing research activities of the major European teams working in Digital Library - related areas with the goal of developing the next generation Digital Library technologies. The focus of our contributions are on Cluster 3: Audio/Visual and Non-Traditional Objects, as well as Cluster 6: Digital Preservation.
MUSCLE
The MUSCLE network, started in March 2004, aims at creating and supporting a pan-European Network of Excellence to foster close collaboration between research groups in multimedia datamining on the one hand and machine learning on the other. The focus of our contribution lies particulalrly in the field of Single Modality Processing, particulalry in the fields of text and audio analysis.
ec3

ec3, founded in 2000 as an industrial competence centre within the so-called
"K-ind programme" of the Austrian Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour,
is a private research association cooperating with business and university
partners to conduct and promote applied research as well as specific projects
in the field of electronic business. ec3 deliberately operates as an intermediary
between science and business practice, building on its multi-disciplinary approach and
based on the high qualification of its research staff covering a broad range of skills.
Within ec3 we are particularly involved with the iSpaces research unit, addressing
all aspects related to the creation, exploration, and understanding of, as well as
interaction with large and potentially heterogeneous multimedia information spaces. A
further area of competence consists in providing partner support in structuring document
repositories, putting documents into a larger context, thus assisting in the discovery and
intuitive retrieval of information. To this end, iSpaces combines exploratory and data analysis
techniques from information retrieval, data mining, user interface design, and information visualization,
to unleash the potential of information available in businesses.
SOMeJB
The SOMeJB system builds upon the principles of the SOMLib system to create a digital library
for music by combining a variety of technologies from the fields of audio processing, neural
networks, and information visualization. It is based on the self-organizing map (SOM),
a popular unsupervised neural network, and its extension, the Growing Hierarchical Self-Organizing Map (GHSOM),
used to organize pieces of music available as, e.g., mp3 files, according to their musical sound characteristics,
i.e. creating a kind of genre-based organization. Islands of Music and Weather Charts provide an intuitive interface to the system.
The project website contains detailed descriptions of the system, source-code for download, as well as demos, allowing you to
browse some of our music collections and listen to excerpts in MP3-format from a wide range of popular and classical music.
SOMLib
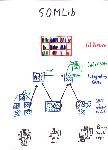
The SOMLIB digital library system supports intuitive, user friendly browsing of document
collections by combining the benefits of conventional library organisation with the possibilities
offered by digital collections.
The SOMLib system builds upon the modules of several sub-projects, specifically the GHSOM neural
network and the libViewer library visualization tool. It is based on the self-organizing map (SOM),
a popular unsupervised neural network, as well as its hierarchical, adaptive extension, the GHSOM.
These neural networks are used to organize documents by content into bookshelves. Metaphor graphics based
on the libViewer system facilitate the intuitive representation of the resulting document archive,
allowing users to get an instant overview of its content and characteristics.
The project website contains detailed descriptions of the system, source-code for
download, as well as demos, allowing you to browse news articles form, e.g. the
Austrian Daily Newspaper "Der Standard", or the Russian News Agency "Nowosti".
libViewer
The cover of a book, the title, type of binding, the shape of the binding
(brand new versus well-used and almost torn apart), the size of the book, color and other properties of
an item on the shelve contain a wealth of information that most people are accustomed to and able to
interpret intuitively. Thus it is easy for us to gain an intuitive overview of the contents of a
library and the type of information present. The libViewer system provides an intuitive user interface
to a digital library by providing a graphical interpretation of metadata. Documents are assigned a
physical representation template such as books, binders, papers etc., with further metadata such as
language, date of last reference etc. being encoded by a set of additional metaphors such as the thickness
of documents, dust, fingerprints, logos and spiderwebs.
Check this project website for the source-code of the system as well as some on-line demos of our prototype
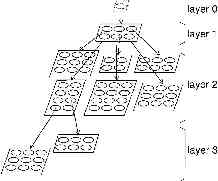
GHSOM
In spite of the stability and popularity of the Self-Organizing Map (SOM),
at least two limitations have to be noted, which are related, on the one hand,
to the static architecture of this model, as well as, on the other hand, to the
limited capabilities for the representation of hierarchical relations of the data.
With our novel Growing Hierarchical Self-Organizing Map (GHSOM) we address both limitations.
The growing hierarchical som is an artificial neural network model with hierarchical architecture
composed of independent growing self-organizing maps. By providing a global orientation of the
independently growing maps in the individual layers of the hierarchy, navigation across branches
is facilitated. The GHSOM is used as a basis for data organization in both the SOMLib and SOMeJB systems,
and forms a core component in the KONTERM project.
AOLA
The amount of information published on the Internet continues to grow at a tremendous rate. Yet, contrary to conventional publications, little of what is published on the World Wide Web is actually preserved in an archive. The need for creating an archive of the information published on the Web, being part of humankind's cultural heritage, while addressing privacy issues, is being recognised by national libraries worldwide, and resulted in the creation of numerous projects. The AOLA project is performed in cooperation with the Austrian National Library (OeNB) and evaluates methods for collecting and preserving the digital cultural heritage of the Austrian Internet.
KONTERM

KONTERM is a research project of the Research Center for Computers and Law, Institute of Public International Law, University of Vienna, Faculty of Law in co-operation with the Institute of Applied Informatics, Department for Informations Systems, University of Vienna, and the Institute of Software Engineering, Technical University of Vienna. It aims at the semiautomatic analysis of legal documents. The SOM and GHSOM neural networks are used to provide content-based organization of legal documents.
GOAL
The GOAL project (EU, INCO-Copernicus, 1998-2001) analysed ways to integrate data warehouses with geographical information systems. Such an integrated system is able to support top executives in their decision-making by providing them with the information stored in the form of geographical information or by mapping data into the geographical domain.