The initial list of lectures and programme are below. Descriptions are below and will be completed shortly. A final schedule will be provided by end of May.
Topics of the different sessions:
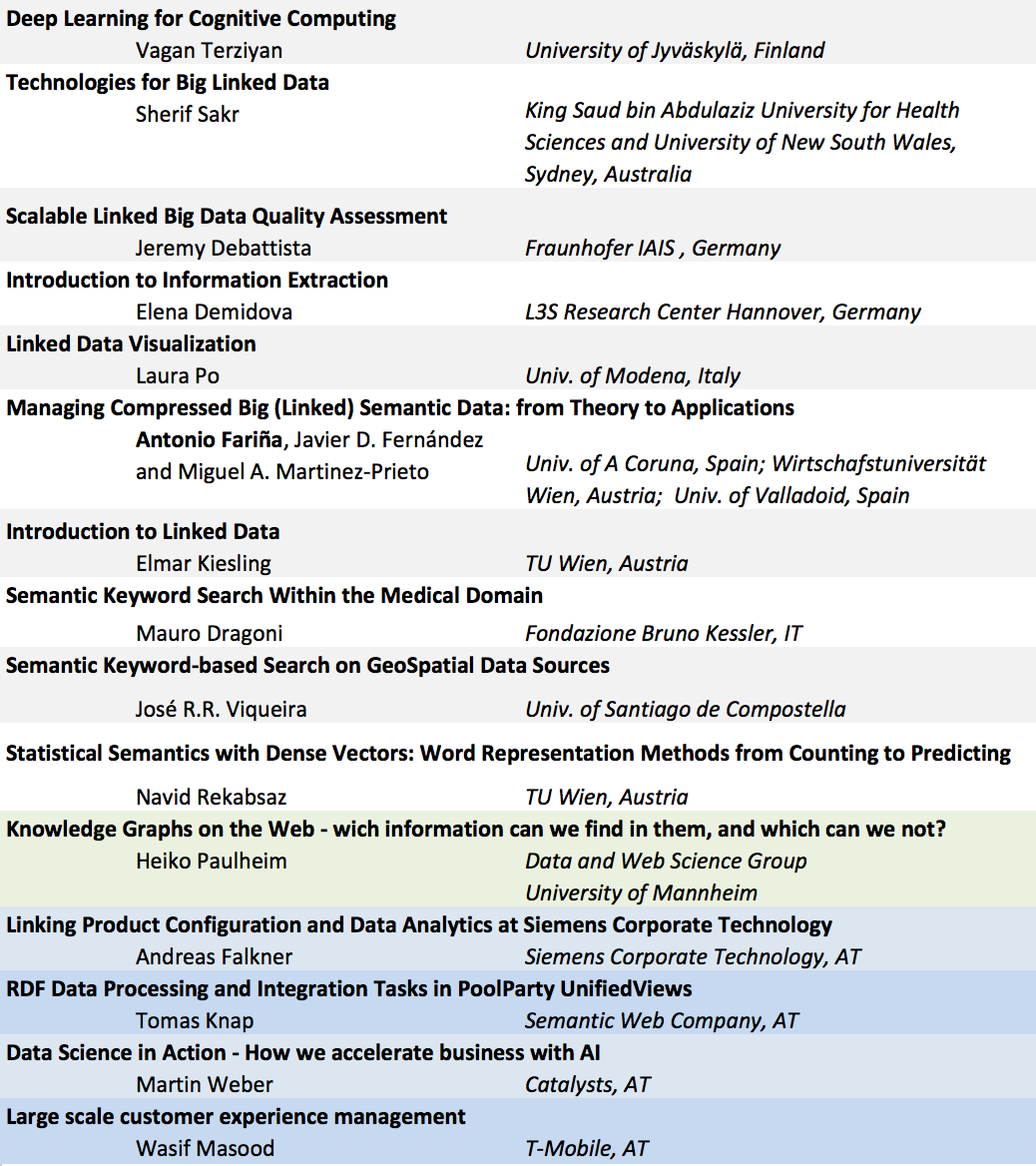
Knowledge Graphs on the Web - wich information can we find in them, and which can we not? (Keynote - Speaker: Heiko Paulheim)
Large-scale, cross-domain knowledge graphs, such as DBpedia, YAGO, or Wikidata, are among the most used structured datasets on the Web. In this talk, I will introduce some of the more prominent ones, including efforts to increase their coverage and quality, as well as new resources, such as the WebIsA database. I will talk about the contents, quality, and overlap of those graphs, and about their subtle differences, giving recommendations on which graph to use for which purpose.
Linking Product Configuration and Data Analytics at Siemens Corporate Technology (Industry speaker: Andreas Falkner)
This talk will cover:
- Who we are: Siemens, Corporate Technology, Research Group "Configuration Technologies"
- What is Product Configuration and what is it good for
- Why we link it with Data Analytics
- How can our joint projects with universities support us
Deep Learning for Cognitive Computing (Tutor: Vagan Terziyan )
The course provides systematic, structured and multidisciplinary view to this popular domain. The major objectives of the course are as follows:
- To describe challenges and opportunities within the emerging Cognitive Computing domain and professions around it;
- To summarize role and relationships of Cognitive Computing within the network of closely related scientific domains and professional fields (e.g., Artificial Intelligence, Semantic and Agent Technologies, Big Data Analytics, Semantic Web and Linked Data; Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, etc.);
- To introduce the major providers of cognitive computing services (Intelligence-as-a- Service) on the market (e.g., IBM Watson, Google DeepMind, Microsoft Cognitive Services, etc.) and show demos of their services (e.g., text, speech, image, sentiment, etc., processing, analysis, recognition, diagnostics, prediction, etc.);
- To give introduction on major theories, methods and algorithms used within cognitive computing services with particular focus on Deep Learning technology;
- To provide “friendly” (with reasonable amount of mathematics) introduction to Deep Learning (including variations of deep Neural Networks and approaches to train them);
- To provide different views to this knowledge suitable to people with different backgrounds and study objectives (ordinary user, advanced user, software engineer, domain professional, data scientist, cognitive analyst, mathematician, etc.);
- To discuss scientific challenges and open issues within the domain as well as to share with the students information on relevant ongoing projects.
Technologies for Big Linked Data (Tutor: Sherif Sakr )
Recently, several systems have been introduced for exploiting this emerging tech- nologies for processing big linked data including HadoopRDF, PigSPARQL, CliqueSquare, S2RDF, SparkRDF, and S2X (SPARQL on Spark with GraphX) engine. The aim of this tutorial is to provide an overview of the state-of-the-art of the new generation of big data processing systems and their applications to linked data domain. In addition, we will highlight a set of the current open research challenges and discuss some promising directions for for future research and development.
Scalable Linked Big Data Quality Assessment (Tutor: Jeremy Debattista)
During the lecture, the participant will understand better the term quality with regard to data. We will also look into a number of state-of-the-art linked data quality frameworks such as Luzzu and RDFUnit, amongst others. Following the linked data quality frameworks, the participants will learn more about the Dataset Quality Vocabulary (daQ) and its follow-up successor; the W3C Data Quality vocabulary. In the second part of the lecture, the participants will be introduced to a number of Linked Data quality metrics. We will then explore different probabilistic techniques that can be used to efficiently compute impractical quality metrics. We will finally give a general overview on the quality of the Web of Data, based on a survey taken on the 2014 version of the LOD Cloud
Introduction to Information Extraction (Tutor: Elena Demidova)
The amount of unstructured information available on the Web is ever growing. Information Extraction enables to automatically identify information nuggets such as named entities, time expressions, relations and events in text and interlink these information nuggets with structured background knowledge. Extracted information can then be used in many application domains, e.g. to categorize and cluster text, enable faceted exploration, populate knowledge bases, and correlate extracted data with other sources. In this introductory tutorial, we provide an overview of the basic blocks for Information Extraction, including methods for named entity extraction and linking, temporal extraction, relation extraction, and open Information Extraction.
Linked Data Visualization (Tutor: Laura Po)
The Linked Data Principles defined by Tim-Berners Lee promise that a large portion of Web Data
will be usable as one big interlinked RDF database.
Today, we are assisting at a staggering growth in the production and consumption of Linked open Data (LOD). Not only researchers and experts but also companies, governments and citizen are finding advantages in using open data.
In this scenario, it is crucial to have tools that provide an overview of the data and support non-technical users in finding and configuring suitable visualizations for a specified subset of the data.
This talk aims at providing practical skills required for exploring LOD sources.
First, we introduce the problem of finding relevant datasets and we define the visualization process. Then we focus on the practical use of LOD/ RDF browsers and visualization toolkits. In particular, we experience the navigation and exploration of some LOD datasets and the construction of different visualizations.
By the end of the talk, the audience will be able to get started with their own experiments on the LOD Cloud.
Managing Compressed Big (Linked) Semantic Data: from Theory to Applications (Tutor: Antonio Farina, Javier D. Fernández and Miguel A. Martinez-Prieto)
This scenario calls for efficient and functional representation formats for RDF as an essential tool for RDF preservation, sharing, and management. In the first part of this lecture, after introducing the main challenges emerging in a Big Semantic (Linked) Data scenario, we will present fundamental concepts of Compact Data Structures and RDF self-indexes. We will analyze how RDF can be effectively compressed by detecting and removing two different sources of syntactic redundancy. On the one hand, RDF serializations (of any kind) waste many bits due to the (repetitive) use of long URIs and literals. On the other hand, the RDF graph structure hides non-negligible amounts of redundancy by itself.
Then, we will introduce HDT, a compact data structure and binary serializa- tion format that keeps big datasets compressed, saving space while maintaining search and browse operations without prior decompression. This makes it an ideal format for storing and sharing RDF datasets on the Web. Besides present- ing its theoretical foundations, we will focus on practical applications and tools, and how HDT is being adopted by the Semantic Web community because of its simplicity and its performance for data retrieval operations. In particular, we will present its successfully deployment in projects such as Linked Data Frag- ments5, which provides a uniform and lightweight interface to access RDF in the Web, indexing/reasoning systems like HDT-FoQ/Jena and LOD Laun- dromat6, a project serving a crawl of a very big subset of the Linked Open Data Cloud.
Finally, we will inspect the challenges of representing and querying evolv- ing semantic data. In particular, we will present different modeling strategies and compact indexes to cope with RDF versions, allowing cross-time queries to understand and analyse the history and evolution of dynamic datasets.
Semantic Keyword Search Within the Medical Domain (Tutor: Mauro Dragoni)
This lecture provides introductory notions for combining semantic technologies and information retrieval strategies in order to improve the effectiveness of keyword-based retrieval systems.
The lecture will focus on the medical domain due to the possibility of exploiting many resources fostering the investigation on this specific task.
The lecture will be split in three parts.
The first part provides an overview of what an ontology is and how it can be used for representing information and for retrieving data. A particular focus will be given also on the linguistic and semantic resources available for supporting this kind of task in the medical domain.
The second part concerns the use of semantic-based retrieval approaches by highlighting the pro and cons of using this kind of approaches with respect to classic ones. Guidelines for the construction of these systems will be provided and examples will be shown.
The third part will present the medical domain as suitable use case. In particular, it will be shown why the medical domain is important for the investigation of semantic information retrieval systems, which are the resources available, and the strategies that could be applied for building effective systems.
Students will be invited to develop systems that could be eventually presented and compared at IKC 2017
Introduction to Linked Data (Tutor: Elmar Kiesling)
Linked Open Data publishing principles are increasingly adopted within the scientific community as well as a by a wide range of governmental and non-governmental institutions, businesses, and citizens of the web at large. Driven by these dynamics, as well as by the rapid commercial adoption of knowledge graphs and embedded web semantics, the web of data has been expanding tremendously in recent years. The resulting global data space creates a wealth of research opportunities and potential for innovative applications.
This introductory tutorial aims to familiarise participants with Linked Data fundamentals and to lay a solid foundation for advanced topics in subsequent sessions. It will first take a brief look back at the history of Linked Data and the Semantic Web and outline the high-level vision for a web of data. Next, it will introduce participants to key principles, concepts, core standards, and protocols -- particularly RDF and SPARQL. Finally, participants will obtain some first hands-on experience in querying and processing Linked Data.
Semantic Keyword-based Search on GeoSpatial Data Sources (Tutor: José R.R. Viqueira)
In general, it is estimated that between 60% and 80% of all the data generated and manipulated by an organization refers to some location in the Earth surface. Due to this, when new advances and technologies arise, their optimization to be applied to geospatial data sources is always one of the first challenges to be faced. If we focus on semantic keyword‐ based search, much research work may be found in the literature related to both Geographic Information Retrieval and the GeoSpatial Semantic Web. This tutorial will provide a short introduction to the representation and management of geospatial data, to provide prior knowledge to cover both Geographic Information Retrieval and GeoSpatial Semantic Web technologies. The tutorial will complete with four examples of challenging problems which are subject of research at the Centro Singular de Investigación en Tecnoloxías da Información (CiTIUS) of the Universidade de Santiago de Compostela (USC), Spain.
Statistical Semantics with Dense Vectors: Word Representation Methods from Counting to Predicting (Tutor: Navid Rekabsaz)
Statistical semantic methods aim to provide a definition of the meanings of the words and their relations, generally by solely using large amount of raw text data. The unsupervised approach of the statistical methods contrast them from knowledge-based ones and facilitates efficiently training of domain- and language-specific semantic models with no need of human-annotation. The semantics of the words is defined by representing each word with a numerical vector representation where the similar words are (computationally) closer to each other in a high-dimensional space. In this course, I review the heuristic and various methods for creating word representations. The course first introduces the initial ideas, based on point mutual information and co-occurrence matrix (count-based) and continues with the state-of-the-art methods using neural networks (prediction-based). We specifically dive into the details of the word2vec algorithm and its subtle characteristics. The course also shows the connection between the count and prediction-based methods. We finally briefly discuss some recent researches on explicit representation and its practical applications.
RDF Data Processing and Integration Tasks in PoolParty UnifiedViews (Tutor: Tomas Knap)
In the last few years, UnifiedViews (http://unifiedviews.eu), became a widely used and accepted solution for management of RDF data processing and integration tasks. PoolParty (https://www.poolparty.biz/) is a world-class semantic technology suite for organizing, enriching, and searching knowledge, which is available on the market for more than 7 years. In my talk, I will briefly introduce UnifiedViews tool, present a demo of UnifiedViews (which will show how users can work with the administration interface of UnifiedViews and how the data processing and integration tasks may be modelled in UnifiedViews), and show 2-3 real use cases in which we used UnifiedViews together with PoolParty Semantic Integrator to help customers to enrich/organize their knowledge base.
Data Science in Action - How we accelerate business with AI (Tutor: Martin Weber)
Catalysts enables customers to speed up their daily business by employing AI in their processes. We demonstrate how different AI mechanisms can team up to deliver seamless customer experience at scale. AI allows our customers to set day to day business on autopilot and move resources from operation to innovation.
Large scale customer experience management (Tutor: Wasif Masood)
Our endures to promote cluster computing has brought us to the era where swift and scalable processing of massively distributed data is no longer privileged to a few. Thanks to the several existing cloud and open source solutions, timely processing of extensive data has now opened new opportunities of growth in business as well as in technology. Customer experience management is one such use case that has emerged as the direct consequence of big data technologies. In this talk, I will give insights about customer experience in telecom domain and how big data is contributing/influencing it.